(We apologize for the recent slow flow of posts on the blog, but we’re spending all our time finishing off our first product for the Private Beta launch and we still haven’t figured out how to extend the 24h limit per day.)
In our last article, Building an IT infrastructure with a sub-3,000 budget we discussed the possibility to build an extremely cheap, yet modern IT infrastructure. Now a couple of weeks later, I’ve actually deployed a setup based on that article.
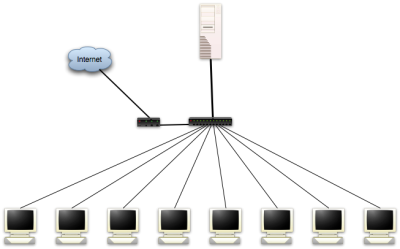
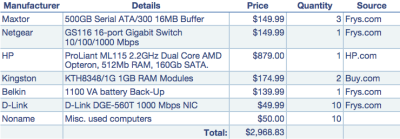
The final system I deployed differed slightly from the specs provided in the previous article. For instance, instead of 10 clients as the article stated, my deployment only included 4 clients (at this point). Other than that, the hardware used was very similar to the article. Below is a list of all the components that was purchased and the approximate price in dollars.
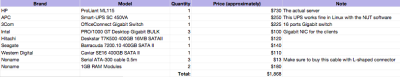
Note that I decided to buy three different brands of hard drives to reduce the chances of having two drives collapse at the same time (two drives from the same batch are more likely to collapse around the same time than two random drives).
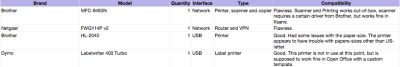
The company already had a handful of semi-obsolete computers that would work fine as clients in the new environment. Also, as in most organizations there were already other peripherals available that I had to make working in this new infrastructure. Fortunately, this went smoother than what I had anticipated. The peripherals were as follows:
The Server
The server is the heart of this environment (as in most environments), therefore, I’ll start describing the setup of the server first. (I’m not really going to describe what LTSP is, and instead kindly refer you to the previous article for an introduction on the topic).
The initial plan, as I described in the previous article, was to install the 64-bit version of Ubuntu 6.06.1 LTS Server on the server, primarily because of the Long Time Support. Unfortunately it turned out to be a bad choice for two reasons:
1) Ubuntu 6.06.1 has quite limited support for LTSP. Although many of the features work fine, some features such as sound-forwarding to the clients are not implemented. It would quite likely be possible to modify the 6.06.1-setup to support sound as well, but I decided to save some time and just switch over to 7.04 server instead.
2) I was forced to use the 32-bit version instead of the 64-bit version. Although I really tried to avoid this, the software support in the 64-bit version didn’t meet my requirements. For instance, I didn’t manage to print from Wine to Cups in the 64-bit version due to some problem with libcups. Moreover, I discovered that there is no Flash support in the 64-bit distribution. Since many websites today require Flash, I had no choice but to use the 32-bit distribution.
So we decided to use the 32-bit version of Ubuntu 7.04 Server. The next problem I came across was how to partition the hard drives. In contrast to what my previous article stated, it turns out that /opt/ltsp/i386 only includes the boot-environment for LTSP, and not the entire system. Therefore it makes little sense to have an 800GB RAID5 array devoted to it. Once the clients have booted up, they log into the core-server. Because of this, I had to change the partitioning strategy. What I ended up doing was to create two partitions on the RAID5 array: one of 795GB to be used for / and one 5GB to be used for swap. I did discover one problem with this setup though: Grub had problems booting off a software RAID array. After some research, I found that it’s possibly to boot Grub from a software RAID, but it required some hacking. Because of this, I decided to create a small partition on the stock hard drive for a /boot and use the remainder of that drive for backup (mounted as /backup). The problem with this setup is that we have a single point of failure – the stock hard drive. Although nothing important is kept on this drive (unless we need to recover our backups), a failure of the drive would still prevent the system from booting.
The hardware
APC Smart-UPS SC 450VA
The only piece of hardware that requires a bit configuration other than the RAID is the UPS. Fortunately setting up this particular brand of UPS is dead simple. Just install the NUT package and modify your configuration files to match the following:
/etc/nut/ups.conf
[ups]
driver=apcsmart
port=/dev/ttyS0
desc="UPS for BLServer1"
sdtype=0
/etc/nut/upsd.conf
ACL all 0.0.0.0/0
ACL remote 192.168.10.0/24
ACL localhost 127.0.0.1/32
ACCEPT localhost
ACCEPT remote
REJECT all
/etc/nut/upsd.users
[monuser]
password = ups_password
allowfrom = localhost
upsmon master
/etc/nut/upsmon.conf
MONITOR ups@localhost 1 monuser ups_password master
and edit /etc/default/nut to
START_UPSD=yes
START_UPSMON=yes
Brother MFC-8460N
Setting up the network printer was a breeze. Just enter the IP address and you’re set. What surprised me a bit was that even the network scanner worked. After installing the Linux driver from Brother’s homepage and following the instructions, the scanner was up and running in less than 5 minutes.
Brother HL-2040
This printer was locally connected, and once it was added in LTSP (see the next section), the printer worked without any problems.
Dymo Labelwriter 400 Turbo
The printer was connected locally to one of the workstations and added without any problems using the pbm2lwxl-driver (ex. CoStar LabelWriter II). I did not spend much time with this printer, but according to openprinting.org the printer is supposed to work fine in OpenOffice with a specific template matching the paper size in the printer.
Setting up LTSP
As described earlier, the way I described LTSP in the prior article was slightly incorrect. Instead of having the entire environment in /opt/ltsp/arch, the clients actually log into the server as if they were local users. Because of this, the first thing we need to do is to install the desktop environment (since the server-edition comes without this). To do this, simply run:
# sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop
Note that this will take quite some time, and I would encourage you to use the installation CD as the source unless you have a very fast internet connection.
Once this is done, it’s time to set up LTSP.
# sudo apt-get install openssh-server
SSH is required to run LTSP, since the traffic from the clients runs through an SSH tunnel
# sudo apt-get install ltsp-server-standalone
Install the LTSP-software
# sudo ltsp-build-clients
Build the client environment. This will take a while.
It’s important that you install the ‘standalone’ edition, else you won’t get the dhcp-server that enables the clients to boot from the actual server. Once you’ve run all the commands above without receiving any errors, you need to make some changes to the dhcp-server. Go ahead and edit /etc/ltsp/dhcpd.conf with your favorite editor to match your network.Then restart the dhcp-server:
# /etc/init.d/dhcp3-server restart
If you changed the IP-address of your server after you ran the installation of ltsp-server-standalone, you need to update the SSH-keys. Do this by running:
# ltsp-update-sshkeys
Setting static IP on clients and allowing local printers
Once you have LTSP configured, you might need to access local devices on the clients. In my case, I had a couple of locally attached printers (both USB and Parallel). To enable the use of these, the first thing you want to do is to set a static IP for the client that holds the printer, based on the MAC address. To do this, we first need to configure the DHCP server to assign a static IP to the client. Edit /etc/ltsp/dhcpd.conf and add:
host ExampleWS1 {
hardware ethernet 00:01:02:03:04:05;
fixed-address 192.168.10.21;
option host-name "ExampleWS1";
}
Now we need to tell LTSP to share the printer assigned to that given workstation. Edit /opt/ltsp/i386/etc/lts.conf and add
[00:01:02:03:04:05] #ExampleWS1
PRINTER_0_DEVICE=/dev/lp0
for sharing a parallel port attached printer, or
[00:01:02:03:04:05] #ExampleWS1
PRINTER_0_DEVICE=/dev/usblp0
for sharing an USB printer.
Once you’ve added this, you need to restart the DHCP server as well as the local client to receive the new IP (or wait for the current IP lease to expire). Now all you need to do is to add the printer using TCP/IP printing with the above IP as the IP address and the appropriate driver for the printer.
That’s it for LTSP. Your server should be ready to have your clients boot off of it now.
Creating a shared space
This part was something that I anticipated to be very simple, but it turned out to be more complex. My plan was to create a folder (/home/shared) and simply just set the owner of that folder to the same group in which I had placed all the desktop users. Although this seemed to work fine at first, a problem appeared when a user created a folder inside of /home/shared. The problem was that all the other users only had read, and not read and write permission to that folder. This means that if User A creates a folder in the shared space, User B cannot rename or delete that folder, which is unlikely to be desirable. After a couple of attempts with chmod, I gave up and started to look for other solutions (correct me if I’m wrong, but it appears as Linux does not inherit folder permission like FreeBSD for instance does). Instead, I found the solution in umask. By editing /etc/profile and changing umask from 022 to 002. What this means is that all files created by the users now have read and write permission by all users in the group. Although this might be considered a security problem, it was the only solution I could find. However, since this is a closed environment, I wouldn’t consider it a very serious problem. Yet, you probably don’t want to have a 002 umask for root and probably want to edit /root/.profile and set umask to 022.
The Clients
Setting up the clients was the easiest part. Just plug in a new Gigabit network adapter and set the BIOS to boot off of it and you’re done. However, I also unplugged the hard drives from the clients to reduce the noise.
The Verdict
Overall the implementation was quite easy. Setting up the LTSP environment was really easy and probably took less than an hour. What I by far spent the most time on was to try to make Wine run the required Windows software (SPCS Administration 2000 Nät). However, after spending about two days hacking configuration files and researching, I threw in the towel – the software just didn’t run well (I primarily blame the software vendor, Visma Spcs, for a very poorly written software with very strange network behavior). Instead, I had to install VMware Server on the Server to run Windows XP (I initially tried Windows 98, since I had a bunch of licenses just laying around, but SPCS Administration 2000 Nät failed to work there too). This was of course undesirable, but with the time constraints I had this turned out to be the only realistic solution. The setup was quite straight forward (using this guide). In order to connect to Windows from the LTSP environment, I simply enabled RDP in Windows and used rdesktop to connect.
The d’oh and ahh’s
* /opt/ltsp/arch only holds the boot environment, not the entire LTSP desktop environment. Once the clients have booted up, they log into the core-server.
* The Windows software that I was supposed to run under Wine didn’t play nice. The only way I got this working was through a Windows XP session running under VMWare Server. Unfortunately this requires a Windows license. However, it’s likely that the company will switch to a web-based program instead, eliminating the requirement.
* I had problems using certain characters when connecting to Windows from the LTSP environment using TightVNC and RealVNC. I solved this problem by switching to Windows’ own RDP-protocol.
Author: Viktor Petersson Tags: Linux,
LTSP,
open source,
Technology,
Ubuntu